Taps Coogan – March 12th, 2023
Enjoy The Sounding Line? Click here to subscribe for free.
Enjoy The Sounding Line? Click here to subscribe for free.
The following article is reposted from Visual Capitalist.
A year on from Russia’s initial invasion of Ukraine, Russian fossil fuel exports are still flowing to various nations around the world.
According to estimates from the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA), since the invasion started about a year ago, Russia has made more than $315 billion in revenue from fossil fuel exports around the world, with nearly half ($149 billion) coming from EU nations.
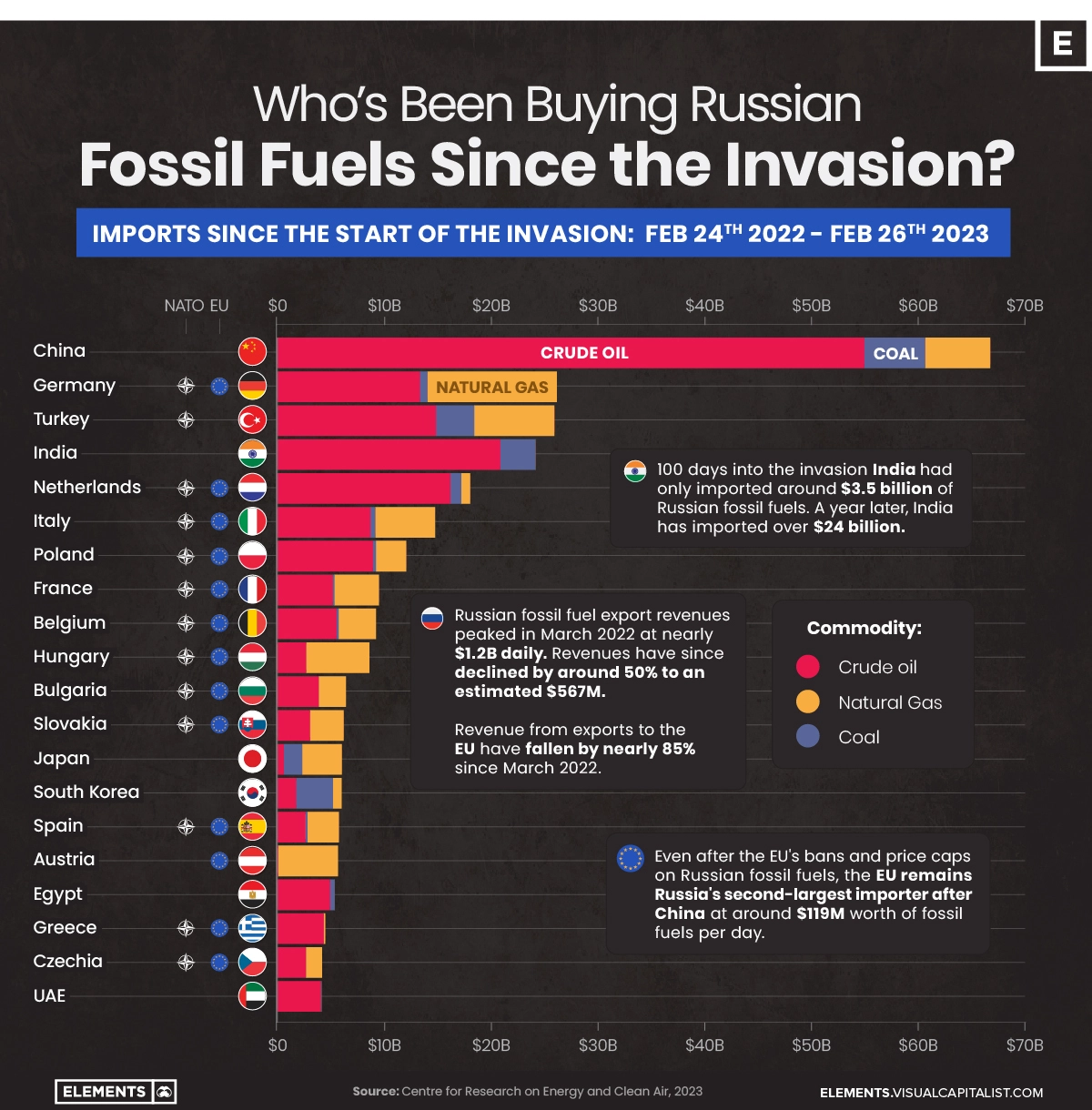
This graphic uses data from the CREA to visualize the countries that have bought the most Russian fossil fuels since the invasion, showcasing the billions in revenue Russia has made from these exports.
Top Importers of Russian Fossil Fuels
As one might expect, China has been the top buyer of Russian fossil fuels since the start of the invasion. Russia’s neighbor and informal ally has primarily imported crude oil, which has made up more than 80% of its imports totaling more than $55 billion since the start of the invasion.
The EU’s largest economy, Germany, is the second-largest importer of Russian fossil fuels, largely due to its natural gas imports worth more than $12 billion alone.
| Country | Total Value of Russian Fossil Fuel Imports* | Crude Oil | Natural Gas | Coal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | $66.6B | $54.9B | $6.1B | $5.7B |
| Germany | $26.1B | $13.3B | $12.1B | $0.7B |
| Turkey | $25.9B | $14.8B | $7.5B | $3.6B |
| India | $24.1B | $20.8B | $0 | $3.3B |
| Netherlands | $18.0B | $16.2B | $0.8B | $1.0B |
| Italy | $14.8B | $8.7B | $5.6B | $0.4B |
| Poland | $12.1B | $8.9B | $2.9B | $0.3B |
| France | $9.5B | $5.2B | $4.2B | $0.2B |
| Belgium | $9.2B | $5.5B | $3.5B | $0.2B |
| Hungary | $8.6B | $2.7B | $5.9B | $0 |
| Bulgaria | $6.4B | $3.9B | $2.5B | $0 |
| Slovakia | $6.2B | $3.1B | $3.1B | $0 |
| Japan | $6.0B | $0.6B | $3.7B | $1.7B |
| South Korea | $6.0B | $1.8B | $0.8B | $3.5B |
| Spain | $5.8B | $2.7B | $2.9B | $0.2B |
| Austria | $5.7B | $0.1B | $5.6B | $0 |
| Egypt | $5.4B | $4.9B | $0 | $0.4B |
| Greece | $4.5B | $4.3B | $0.2B | $0 |
| Czechia | $4.2B | $2.7B | $1.5B | $0 |
| UAE | $4.1B | $4.1B | $0 | $0.1B |
*Over the time period of Feb 24, 2022 to Feb 26, 2023 in U.S. dollars
Turkey, a member of NATO but not of the EU, closely follows Germany as the third-largest importer of Russian fossil fuels since the invasion. The country is likely to overtake Germany soon, as not being part of the EU means it isn’t affected by the bloc’s Russian import bans put in place over the last year.
Although more than half of the top 20 fossil fuel importing nations are from the EU, nations from the bloc and the rest of Europe have been curtailing their imports as bans and price caps on Russian coal imports, crude oil seaborne shipments, and petroleum product imports have come into effect.
Russia’s Declining Fossil Fuel Revenues
The EU’s bans and price caps have resulted in a decline of daily fossil fuel revenues from the bloc of nearly 85%, falling from their March 2022 peak of $774 million per day to $119 million as of February 22nd, 2023.
Although India has stepped up its fossil fuel imports in the meantime, from $3 million daily on the day of the invasion to $81 million per day as of February 22nd of this year, this increase doesn’t come close to making up the $655 million hole left by EU nations’ reduction in imports.
Similarly, even if African nations have doubled their Russian fuel imports since December of last year, Russian seaborne oil product exports have still declined by 21% overall since January according to S&P Global.
Other Factors Impacting Revenues
Overall, from their peak on March 24th of around $1.17 billion in daily revenue, Russian fossil fuel revenues have declined by more than 50% to just $560 million daily.
Along with the EU’s reductions in purchases, a key contributing factor has been the decline in Russian crude oil’s price, which has also declined by nearly 50% since the invasion, from $99 a barrel to $50 a barrel today.
Whether these declines will continue is yet to be determined. That said, the EU’s 10th set of sanctions, announced on February 25th, ban the import of bitumen, related materials like asphalt, synthetic rubbers, and carbon blacks and are estimated to reduce overall Russian export revenues by almost $1.4 billion.
Would you like to be notified when we publish a new article on The Sounding Line? Click here to subscribe for free.

